HOW TO ESTIMATE LANDSLIDE HAZARDS USING SIMPLE MODEL?
CASE STUDY OF BANTUL REGENCY, YOGYAKARTA PROVINCE
A landslide or landslip is a geological phenomenon which includes a wide range of ground movement, such as rock falls, deep failure of slopes and shallow debris flows, which can occur in offshore, coastal and onshore environments. Although the action of gravity is the primary driving force for a landslide to occur, there are other contributing factors affecting the original slope stability. Typically, pre-conditional factors build up specific sub-surface conditions that make the area/slope prone to failure, whereas the actual landslide often requires a trigger before being released.
Landslides occur when the stability of a slope changes from a stable to an unstable condition. A change in the stability of a slope can be caused by a number of factors, acting together or alone. Natural causes of landslides include:
- groundwater (porewater) pressure acting to destabilize the slope
- loss or absence of vertical vegetative structure, soil nutrients, and soil structure (e.g. after a wildfire)
- erosion of the toe of a slope by rivers or ocean waves
- weakening of a slope through saturation by snowmelt, glaciers melting, or heavy rains
- earthquakes adding loads to barely-stable slope
- earthquake-caused liquefaction destabilizing slopes
- volcanic eruptions
Landslides are aggravated by human activities, Human causes include:
- deforestation, cultivation and construction, which destabilize the already fragile slopes
- vibrations from machinery or traffic blasting
- earthwork which alters the shape of a slope, or which imposes new loads on an existing slope
- in shallow soils, the removal of deep-rooted vegetation that binds colluvium to bedrock
- construction, agricultural or forestry activities (logging) which change the amount of water which infiltrates the soil.
Required Data and Methods
- Required Data
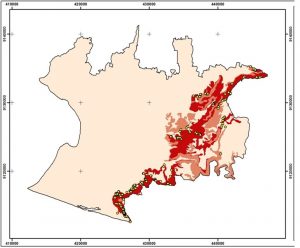
Example of required data for estimating landslide data area boundaries, previous landslide information, and slope information.
- Methods
Method used in this tutorial is to calculating coverage area of landlside using ArcGIS software. This method is done by by looking at previous landslide occurrence data, more landslide occurred in the area also will be increasingly prone to landslides. then the data is compared with the slope classes. assumed that the higher slopes also more prone to landslides. Slope was classified and previous landslide point density into three classes respectively. Both parameter overlaid and processed to get final rank for each area.
Result